Signed-off-by: bijayasharma <vetbijaya@gmail.com> Change-Id: I5d453720a586368d7ca37536511c0043fd418fde
12 KiB
System Requirement and Setup
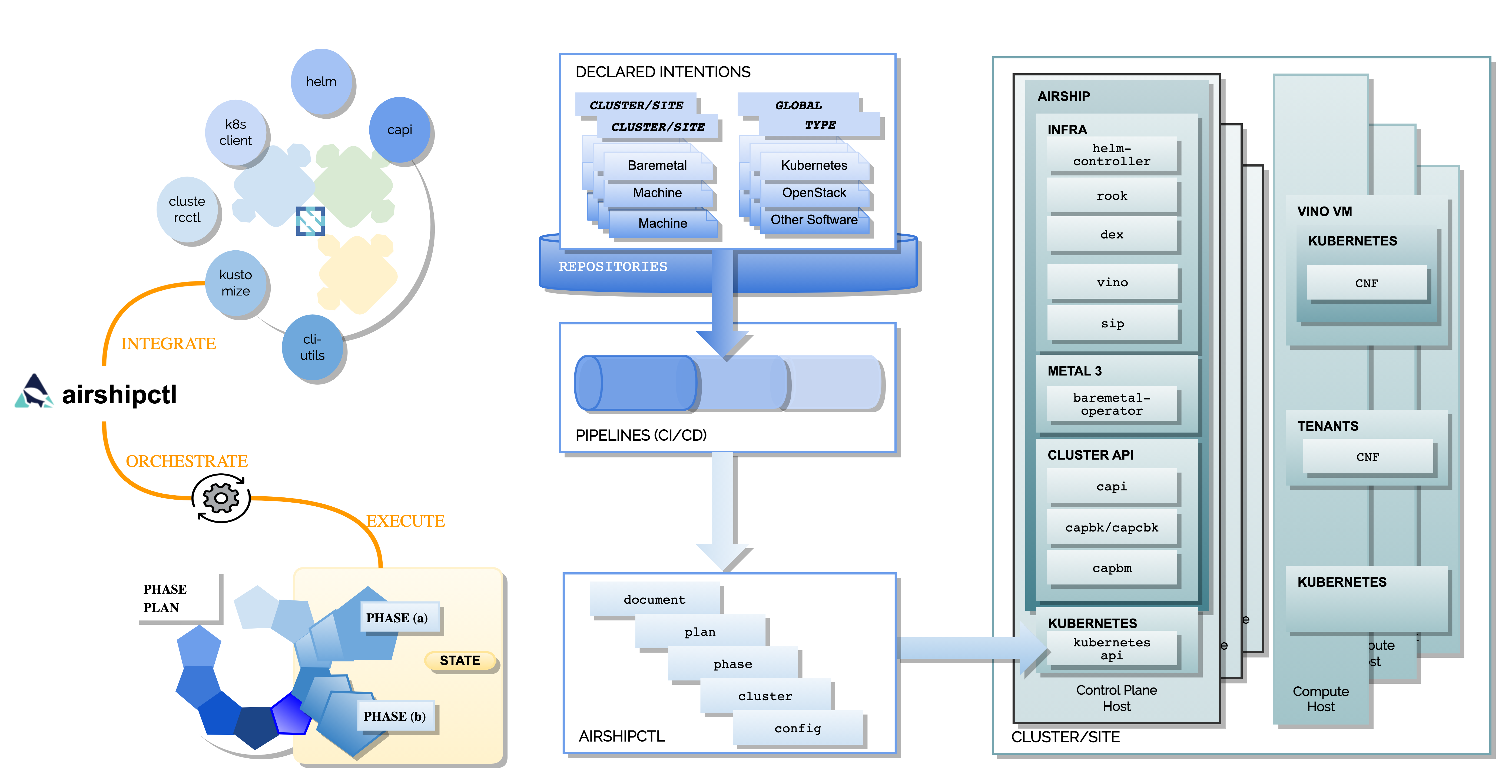
Component Overview
Airship uses a command line utility airshipctl that drives the deployment and life cycling management of Kubernetes clouds and software stacks.
This utility articulates lifecycle management as a list of phases, or as a plan of phases or plan. For each of these phases, a YAML document set is rendered and Airshipctl transparently utilizes the appropriate set of CNCF projects to deliver that particular phase.
Node Overview
This document refers to several types of nodes, which vary in their purpose, and to some degree in their orchestration / setup:
- Build node: This refers to the environment where configuration documents are built for your environment (e.g., your laptop).
- Ephemeral node: The "ephemeral" or "seed node" refers to a node used to get a new deployment off the ground, and is the first node built in a new deployment environment.
- Controller nodes: The nodes that make up the control plane. (Note that the ephemeral node will be converted to one of the controller nodes).
- Worker nodes: The nodes that make up the data plane.
Hardware Preparation
The Treasuremap reference-airship-core site shows a production-worthy bare metal deployment that includes multiple disks and redundant/bonded network configuration.
Note
Airship hardware requirements are flexible, and the system can be deployed with very minimal requirements if needed (e.g., single disk, single network).
For simplified non-bonded, and single disk examples, see Treasuremap test-site.
BIOS, Redfish and PXE
- Ensure that virtualization is enabled in BIOS.
- Ensure that Redfish IPs assigned, and routed to the environment you will deploy into. Firmware bugs related to Redfish are common. Ensure you are running the latest firmware version for your hardware.
- Set PXE as first boot device and ensure the correct NIC is selected for PXE.
Note
* Airship can remotely bootstrap the nodes using Redfish. If Redfish is not available, you can mount the ephemeral ISO image via an alternate mechanism such as USB thumb drive. * Airship 2 has been verified on Dell PowerEdge R740xd servers with iDRAC 9, BIOS Version 2.8.2, iDRAC Firmware Version 4.22.00.53 and Redfish API version 1.
Disk
- For controller nodes including the ephemeral node:
- Two-disk RAID-1: Operating System
- For worker nodes (tenant data plane):
- Two-disk RAID-1: Operating System
- Remaining disks: configuration per worker host profile
Note
As of release v2.0.0, the reference-airship-core example
does not support the integration with the Rook Storage Operator. However, the
manifests for the Rook deployment can be found in the
manifests/function/rook-operator directory. If you plan to
include Rook for Ceph storage, it is recommended to have the additional
disks on all the controller nodes and worker nodes:
- Two disks JBOD: Ceph Journal and Metadata
- Two disks JBOD: Ceph OSD's
Network
- Ensure that you have a dedicated PXE interface on untagged/native VLAN. 1x1G interface is recommended. The PXE network must have routability to the internet in order to fetch the provisioning disk image; alternately, you may host the image locally on the PXE network itself.
- Ensure that you have VLAN segmented networks on all nodes. 2x25G bonded interfaces are recommended.
The table below is an opinionated example used by Treasuremap
reference site reference-airship-core, but users can
diverge from it as needed. For example, in the simplest configuration,
two networks can be configured: one for PXE and one for everything
else.
| VLAN/ Network | Name | Routability | Quantity | MTU | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
IPv4:/26 IPv6:/64 | 1500 | For HW Redfish addressing |
|
|
|
IPv4:/25 IPv6:/64 | 1500 | For bootstrap by Ironic, Metal3 or MaaS |
|
|
|
IPv4:/26 IPv6:/64 | 9100 |
|
|
|
IPv4:/29 | 9100 |
|
|
|
|
|
IPv4:/25 IPv6:/64 | 9100 | Ceph storage traffic for all hosts, pods and VMs |
|
|
|
IPv4:/25 IPv6:/64 | 9100 | L2 network used by Calico for BGP peering or or IP-in-IP mesh |
|
|
|
IPv4:/22 IPv6:/64 | 9100 | Private IP ranges to VM based subclusters for K8S as a service |
| Private Reserve |
|
Zone Private | IPv4:/16 IPv6:/64 | N/A | For Kubernetes Pods and objects by Calico |
| Private Reserve |
|
Zone Private | IPv4:/16 IPv6:/64 | N/A | For K8S service objects and intermediary pods |
See detailed network configuration example in the Treasuremap repo
manifests/site/reference-airship-core/target/catalogues/networking.yaml
configuration file.
Hardware sizing and minimum requirements
| Node | Disk | Memory | CPU |
|---|---|---|---|
| Build (laptop) |
|
|
|
| Ephemeral/Control |
|
|
|
| Worker |
|
|
|
- Workload driven (determined by host profile)
See detailed hardware configuration in the Treasuremap repo
manifests/site/reference-airship-core/target/catalogues
folder.
Establishing build node
Setting Environment Variables
The Airship deployment tool requires a few environment variables that the operators need to configure on the build node. The environment variables can be persisted by setting them in your profile, or can be set in the shell session before you run the Airship commands and scripts.
Proxy
Access to external resources such as github,
quay.io and go is required for downloading
manifests, images and go packages. If you are behind a
proxy server, the following environment variables must be configured on
the build node.
USE_PROXY: Boolean value to indicate if the proxy setting should be used or not.http_proxy: Proxy server for HTTP traffic.https_proxy: Proxy server for HTTPS traffic.no_proxy: IP addresses or domain names that shouldn’t use the proxy.
SOPS
For security reasons the secrets in the Airship manifests should not be stored in plain-text form. Airshipctl selects Mozilla SOPS to encrypt and decrypt the manifests.
Two environment variables are needed for the encryption and decryption:
SOPS_IMPORT_PGP: Contains public or private key (or set of keys).SOPS_PGP_FP: Contains a fingerprint of the public key from the list of provided keys inSOPS_IMPORT_PGPthat will be used for encryption.
The easiest way to generate SOPS keys is to use gpg wizard:
gpg --full-generate-keyFor demo purpose, you can import the pre-generated SOPs keys used by Airshipctl gate:
curl -fsSL -o /tmp/key.asc https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mozilla/sops/master/pgp/sops_functional_tests_key.asc
export SOPS_IMPORT_PGP="$(cat /tmp/key.asc)"
export SOPS_PGP_FP="FBC7B9E2A4F9289AC0C1D4843D16CEE4A27381B4"Airship Installation
AIRSHIP_CONFIG_MANIFEST_DIRECTORY: File system path to the Airship manifest directory, which will be the home of all Airship artifacts, including airshipctl, treasuremap, your projects and sites. You can create the directory at a location of your choice.PROJECT: Name of the project directory to be created in theinit_sitesection.SITE: Name of the site to be deployed.
Download Airshipctl
- On the build node, install the Git package:
sudo apt update
sudo DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt -y install git- Create the Airship home directory and clone the
airshipctlrepository:
mkdir -p $AIRSHIP_CONFIG_MANIFEST_DIRECTORY
cd $AIRSHIP_CONFIG_MANIFEST_DIRECTORY
git clone https://opendev.org/airship/airshipctl.git
cd airshipctl && git checkout <release-tag|branch|commit-hash>Install Essential Tools
Install the essentials tools, including kubectl, kustomize, pip, and yq.
From the airshipctl directory, run:
./tools/deployment/10_install_essentials.sh
# Recommend to add the user to the docker group
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER- Install airshipctl executable.
./tools/deployment/21_systemwide_executable.sh(Optional) Install Apache Web server.
Airship 2 deployment requires a web server to host the generated ephemeral ISO image. If you don't have an existing web server, you can install an Apache server on the build node.
sudo apt install apache2Note
The Apache Web server must be accessible by the ephemeral host.
After the build node is established, you are ready to start creating your site manifests and deploying the site.